The Common Vein Copyright 2008
Definition
Acalculous cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder, that is not related to stone disease and is primarily and initially a consequence of atony of the gallbladder caused by prolonged fasting and a consequent lack of CCK stimulation. The patients who have prolonged stay in the ICU and more specifically those who have sustained burns, trauma, or major surgical intervention – all entities that require prolonged ICU courses, are at risk for this enity. Although it often occurs in the inpatient setting, it may occasionally occur as an outpatient. Patients with hyperemesis gravidarum can present with acalculous cholecystitis.
Structurally the gallbladder shows distension and is without cholelithiasis. The failure of CCK stimulation from normal diet results in a gallbladder that is atonic, which becomes distended since bile is continually produced and not distributed.
Functionally the gallbladder is atonic and fails to transport the bile to the ampulla.
The tension on the wall renders it ischemic and susceptible to infarction, infection and bile infiltration. Hence cholecystitis supervenes.
The clinical presentation is usually a patient in the ICU who has a fever of unknown origin or who has right upper quadrant pain or tenderness with a positive Murphy’s sign.
From an imaging standpoint, ultrasound is the study of choice since. It shows findings similar to acute cholecystitis but no stones are present. The gallbladder is distended, the wall may be thickened, there may be fluid in the gallbladder fossa. Hyperemia is usually present, and probe tendernesss is commonly elicited when the patient is concious and communicative. CT is also useful particulalrly for the evaluation of changes in the surrounding fat which if present would suggest rupture of the wall..
Acalculous cholecystitis may complicated by gangrenous changes in the wall which could manifest radiologically with exteremely thin walls, empyema, abscess formation or perforation with bile peritonitis.
Acalculous cholecystitis is best treated with percutaneous cholecystostomy, which serves to decompress the gallbladder.
Early Stage of Cholestasis – Thin Sludge |
| In the early stages of cholestasis the bile becomes thickened, and sinks to dependant portions of the gallbladder. Since the SG is still fairly close to bile a fluid fluid level exists.
Ear11921.8b05b039.8s gallbladder distended enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge cholestasis stasis Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
Tumefactive Bile |
| With continued cholestasis due to atony from lack of CCK stimulation, more water is absorbed from the bile and a thicker sludge evolves. The SG of the bile becomes even greater and the bile now has the consistency of mud and forms tumefactive bile. The character of the sludge now takes on its own shape and has mass like appearance – hence tumefactive. The color of the bile in the gallbladder and the sludge darkens.
11921.8b05b043..8sb01 gallbladder distended tumefactive bile crank case oil thick sludge enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge black cholestasis stasis Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
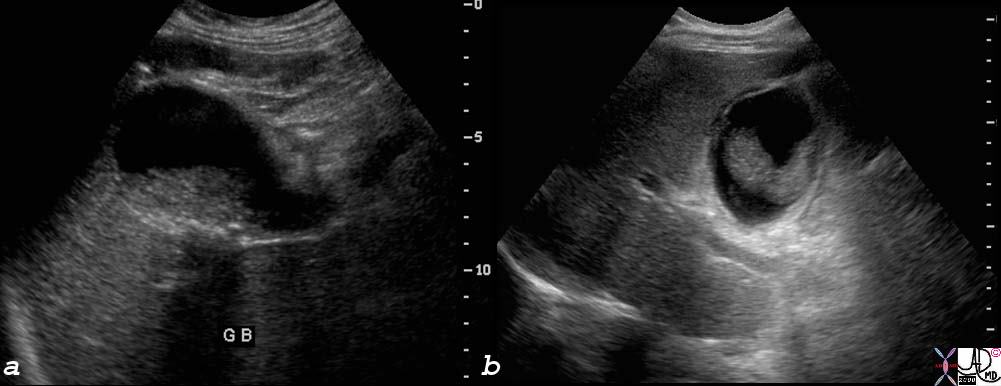 RUQ Pain, Distended Gallbladder, Tumefactive Bile RUQ Pain, Distended Gallbladder, Tumefactive Bile |
| The longitudinal view and transverse view of the gallbladder show mass like tumefactive bile. This is a sign of advancing cholestasis. The wall is not thickened and there is no fluid in the gallbladder fossa. Cholestasis and not cholecystitis is apparrent.
77717c01s right upper quadrant pain ICU setting RUQ pain gallbladder distended thick walled sludge cholestasis tumefactive bile fluid in gallbladder fossa small shadowing stones acalculous cholecystitis shape of tumefactive bile in the gallbladder has fetus like formation USscan ultrasound Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
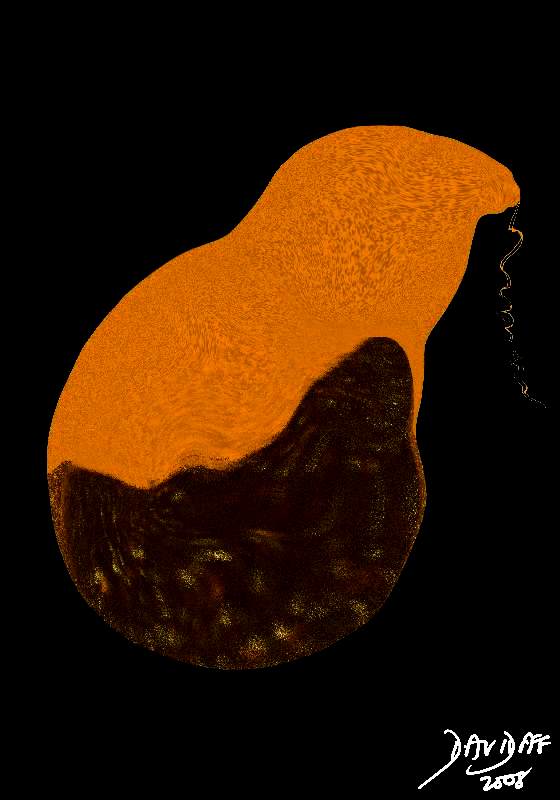
 Acalculous Cholecystitis Crankcase Oil Acalculous Cholecystitis Crankcase Oil |
| Pressure on the wall of the gallbladder causes ischemia and inflammation ensues. The diagram shows an inflamed wall (red) and the bile thickened tumefactive bile is becoming blacker in color. This color has been likened to crankcase oil in its color.
11921.8b05b043.8s gallbladder distended tumefactive bile thick sludge enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge cholestasis stasis inflammation acalculous cholecystitis Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
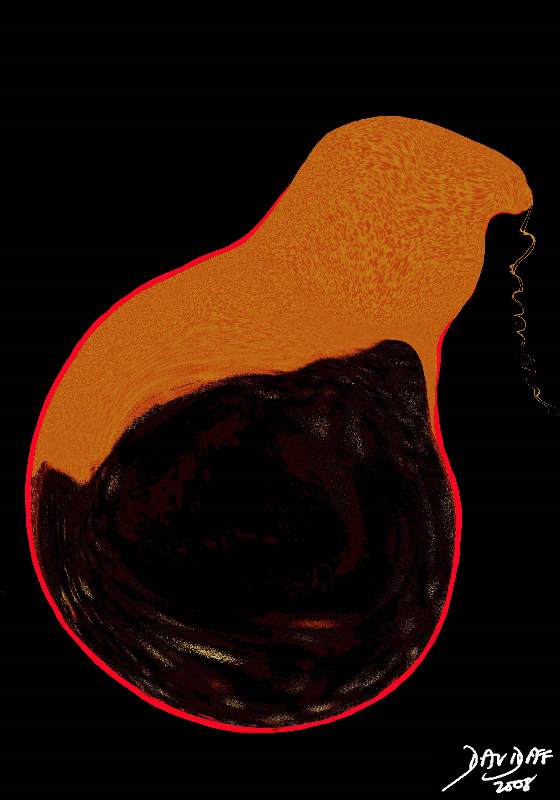
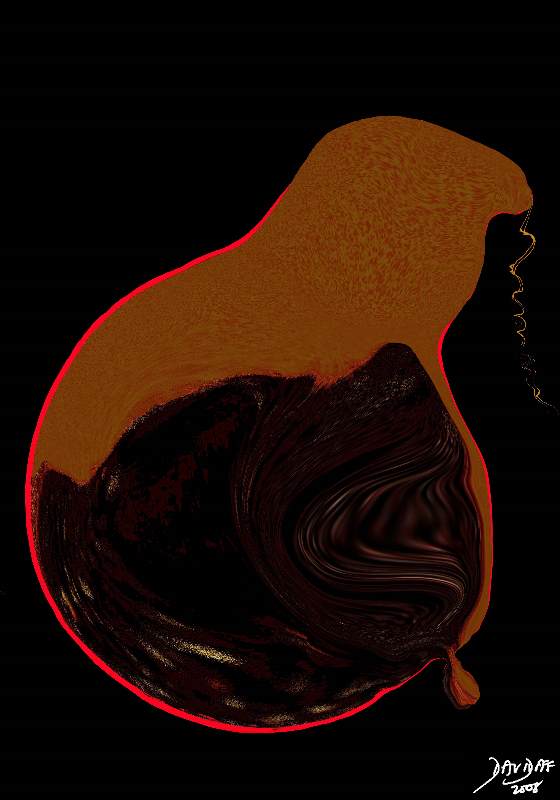 Wall Rupture Wall Rupture |
| 11921.8b05b043..8kb03 gallbladder distended tumefactive bile crank case oil thick sludge enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge black cholestasis stasis wall inflammation acalculous cholecystitis complicated by perforation Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
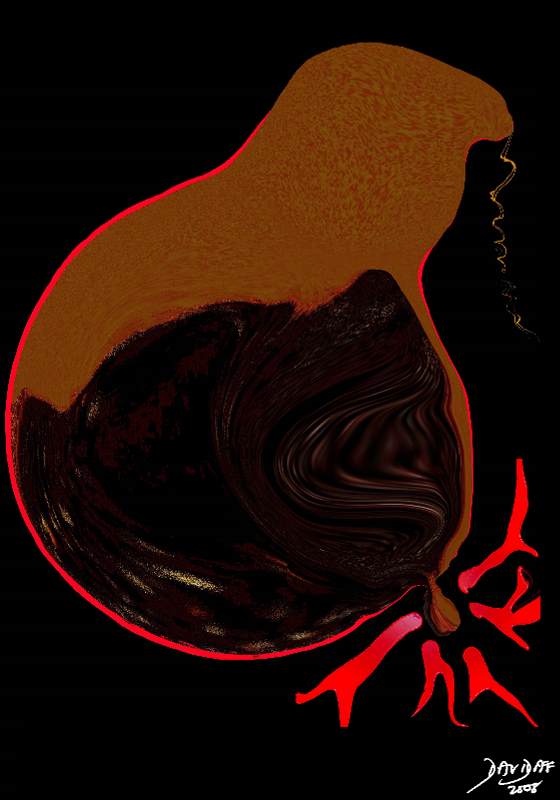

Wall Rupture Focal Peritonitis |
| If left untreated the wall can break down leading to leakage of bile into the peritoneal cavity causing bile peritonitis which is potentially lethal. The diagram shows leakage of bile into the peritoneal cavity and a severe rective inflammatory response.
11921.8b05b043.8b05s gallbladder distended tumefactive bile crank case oil thick sludge enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge black cholestasis stasis wall inflammation acalculous cholecystitis complicated by perforation Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
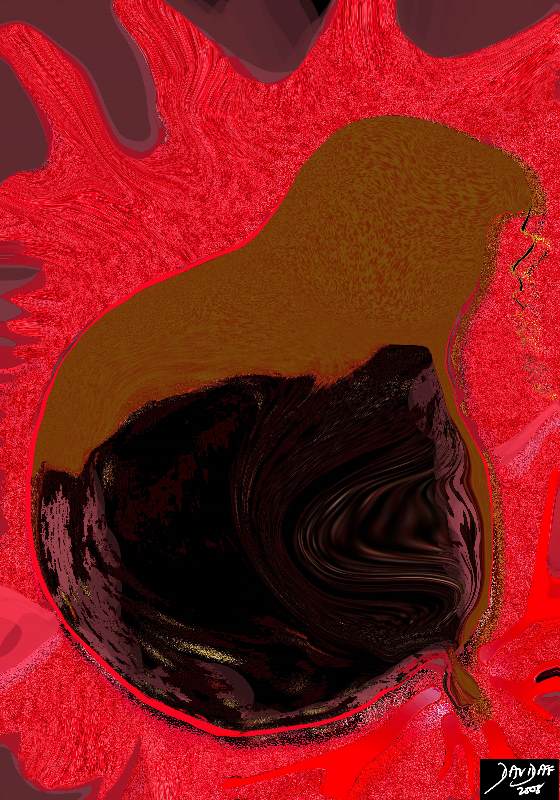
Rupture with Diffuse Bile Peritonitis |
| If left untreated the wall can break down leading to leakage of bile into the peritoneal cavity causing bile peritonitis which is potentially lethal. The diagram shows leakage of bile into the peritoneal cavity and a severe rective inflammatory response.
11921.8b05b046.8b05 gallbladder distended tumefactive bile crank case oil thick sludge enlarged dilated fluid fluid level gravity specific gravity sediment sludge black cholestasis stasis wall inflammation acalculous cholecystitis complicated by perforation and bile peritonitis Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
RUQ Pain, Distended Gallbladder, Indurated Fat |
| 77717c02s right upper quadrant pain ICU setting RUQ pain gallbladder distended thick walled hyperemic enhancing wall pericholecystic induration dirty fat stranding acalculous cholecystitis Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
Release of bile salts is dependent upon CCK release. In the case of impaired secretion (such as in ICU patients), this can lead to several different pathologies, among which is non-calculus cholecystitis.<!–[if !supportFootnotes]–>
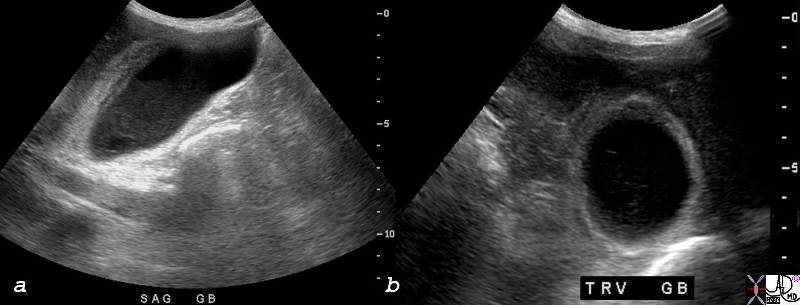
Acaclculous Cholecystitis |
| 77680c01.8 right upper quadrant pain RUQ pain ICU setting gallbladder distended sludge cholestasis complex fluid in the gallbladder fossa acalculous cholecystitis USscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
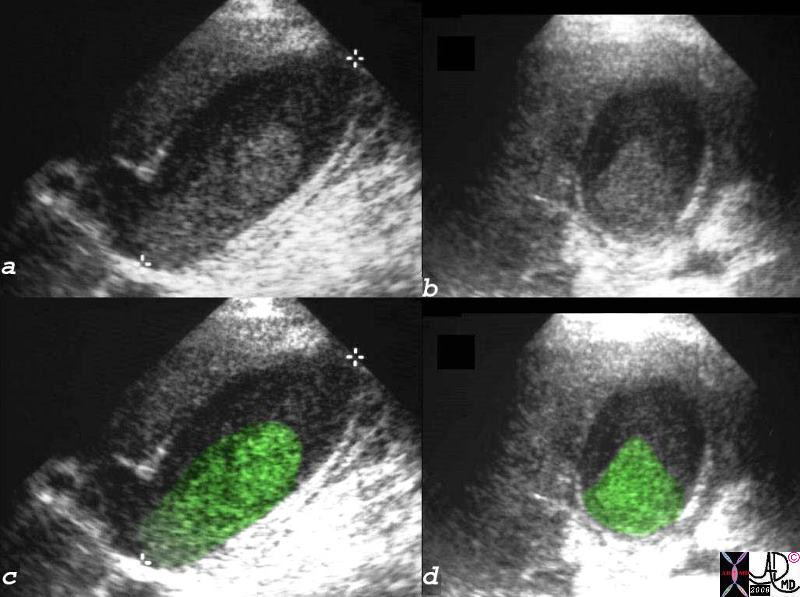
Acaclculous Cholecystitis |
| 16136c03.8s gallbladder prolonged ICU stay right upper quadrant pain right upper quadrant tenderness cholestasis enlarged tumefactive bile sludge thick walled acalculous cholecystitis percutaneous cholecystostomy ultrasound USscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
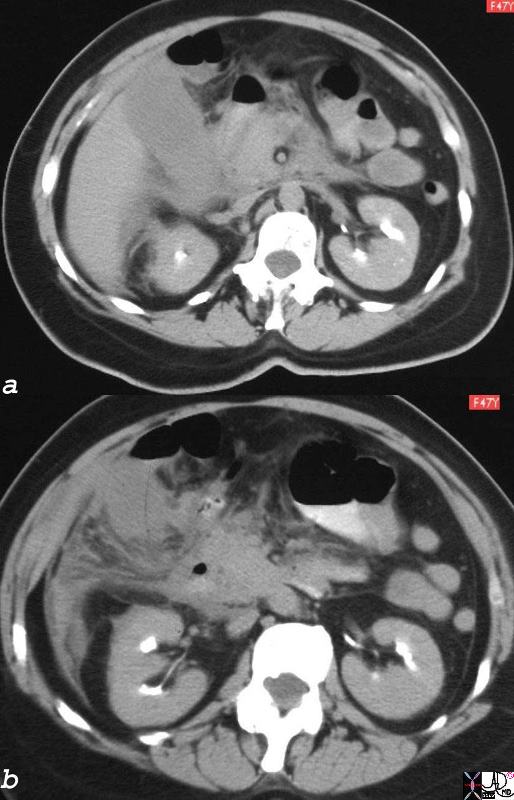
Ruptured Gallbladder |
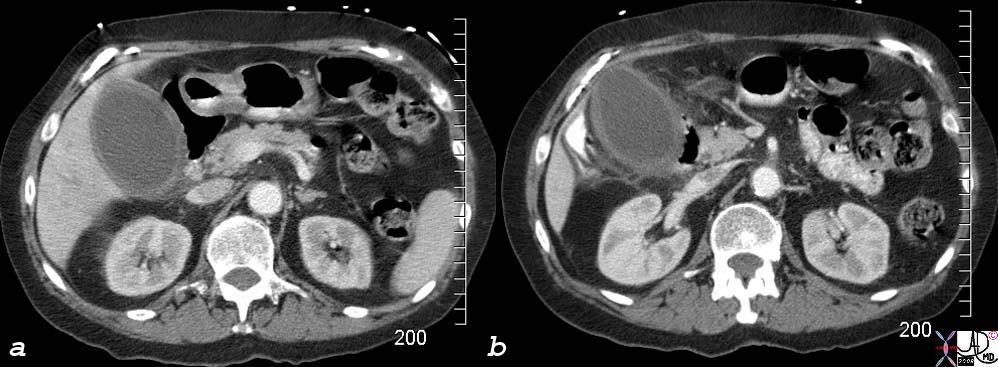
| The 47 year old female had acalculous cholecytitis which progressed to rupture of the gallbladder. The CT scan shows significant induration of the fat around the gallbladder and some free fluid Morrison’s pouch. Bile peritonitis ensued.
27222c01.8s 47F gallbladder indurated fat fluid anterior pararenal space Morrisons pouch perirenal space acalculous cholecystitis rupture perforation flattened IVC inferior vena cava dehydration decreased intravascular volume Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
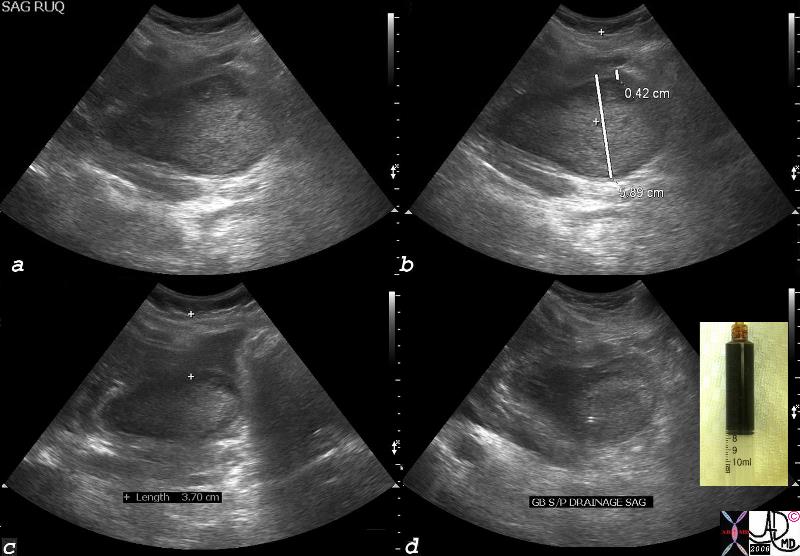
Acalculous Cholecystitis and Crankcase Oil |
|
The US scan is from a 32 year old pregnant female with hyperemesis gravidarum who presented with right upper quadrant pain, a distended gallbladder and tumefactive bile. A percutaneous catheter was pl;aced using US as a guide. Image a shows gallbladder distended with thick bile, while image b shows the transverse diameter measured at 5.89cms which is abnormally large, (normal usually up to 4cms) while image c, shows the depth of the gallbladder from the skin in preparation for catheter placement. Image d shows a double echogenic shadow (like a small tramtrack) representing the catheter in the gallbladder. The bile that came out was black like the bile in the syringe, and reminiscent of crank case oil. The appearance is characteristic for acalculous cholecystitis. and a distensded gallbladder26067c01.8cs gallbladder acalculous cholecystitis percutaneous cholecystostomy crankcase oil black bile CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
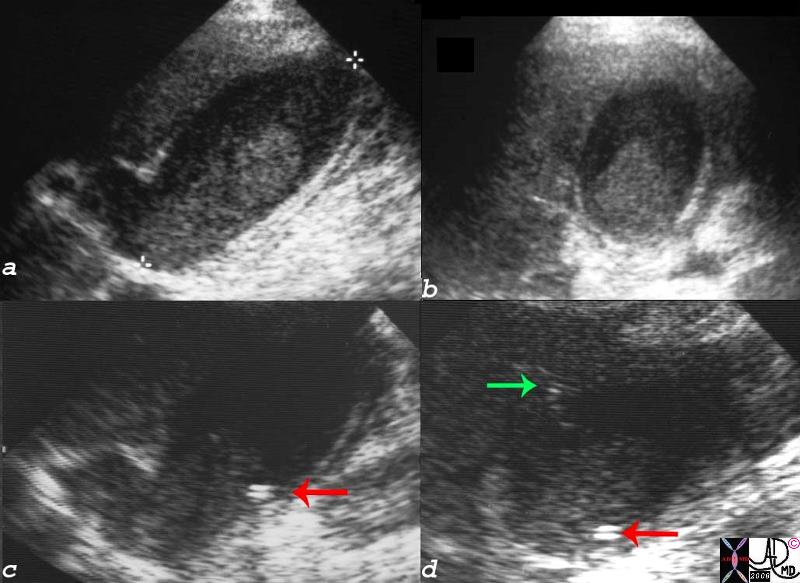
Acaclculous Cholecystitis with Cholecystostomy tube in Place |
| 16136c01.8s gallbladder prolonged ICU stay right upper quadrant pain right upper quadrant tenderness cholestasis enlarged tumefactive bile sludge thick walled acalculous cholecystitis percutaneous cholecystostomy ultrasound USscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
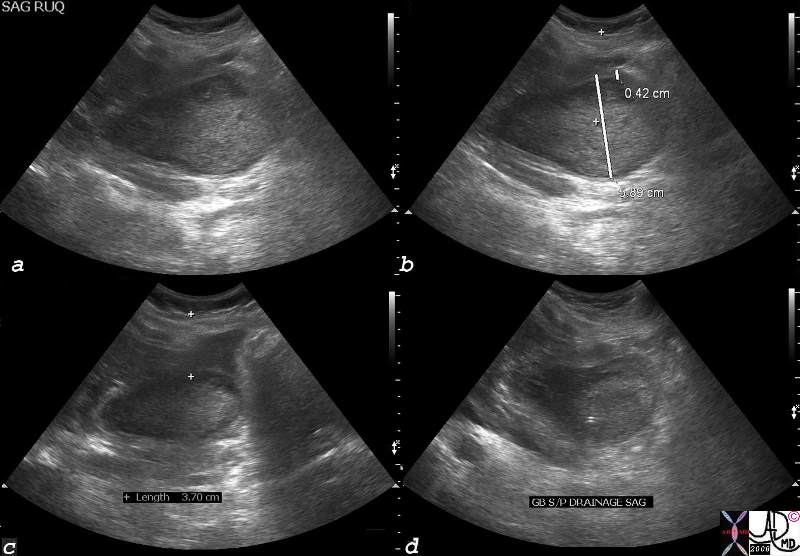
Hyperemesis Gravidarum and Acalculous Cholecytitis |
| 77695c04.8s 32 female pregnant with hyperemesis gravidarum gallbladder distended painful sludge tumefactive bile percutaneous cholecystostomy USscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
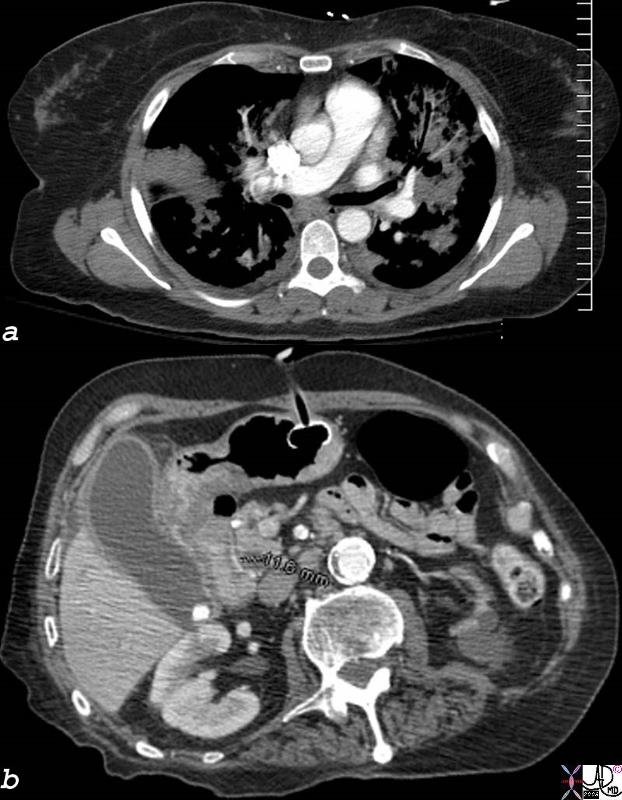
Acalculous or Calculous Cholecystitis? |
| 78335c01.8s elderly female in ICU setting with pneumonia and ARDS and gastrostomy feeding tube. CTscan shows gallbladder distended and enlarged hyperemic thickened wall induration in the fat around the gallbladder gall stone cholelithiasis differential diagnosis includes acaclculous cholecystitis and calculous cholecystitis CTscan Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff copyright 2008 |
