The Common vein Copyright 2008
Definition
Cholesterolosis is proliferative disorder of the gallbladder mucosa and is part of a disease group called the hyperplastic cholecytoses
The cause of the entity is not known but it occurs more commonly in females in 4th-5th decade and is seen commonly (30%) of cholecystectomy specimens.
The result is the deposition of lipid, comprised of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in macrophages within the lamina propria and mucosa. Aberrant cholesterol metabolism and the subsequent sequestration of lipids in macrophages (foam cells) is a process similar to that in atherosclerosis, but is of unknown clinical significance in the gallbladder.
Structurally there may be localized accumulation or diffuse distribution. In the localized form the polyps can vary in size from 1-10mms. The polypoid form may demonstrate echoes projecting into the lumen of the gallbladder.
In the diffuse form the yellow accumulations are often seen in the background of a hyperemic mucosa pathologically so that the appearance macroscopically is reminiscent of a strawberry. (“strawberry gallbladder”)
There seems to be no definite functional nor clinical significance to the entity.
The diagnosis is often made by US scan or CT. US has a fairly characteristic appearance. The polyps are seen as echogenic foci in or on the mucosa, and the polyps show no shadowing and are attached to the wall of the gallbladder.
The entity is not usually treated since most believe there is no clinical significance. In patients with right upper quadrant pain that cannot be explained and who have cholesterolosis some data suggests that cholecystectomy may be beneficial
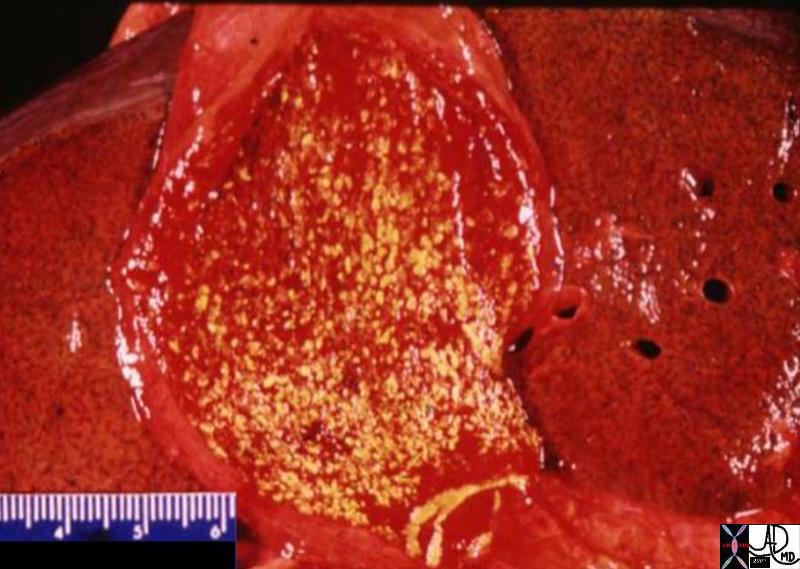
Strawberry Gallbladder |
| The pathological specimen shows diffuse form of cholesterolosis with a bed of focal fat accumulations (yellow) in a backrgound hyperemic mucosa, reminiscent of the skin of a strawberry.
04777.800 gallbladder strawberry gallbladder hyperemic mucosa yellow cholesterolosis hyperplastic cholecystoses cholecytosis Davidoff MD hyperplastic cholecystosis hyperplastic cholecystoses adenomyomatosis cholesterolosis |
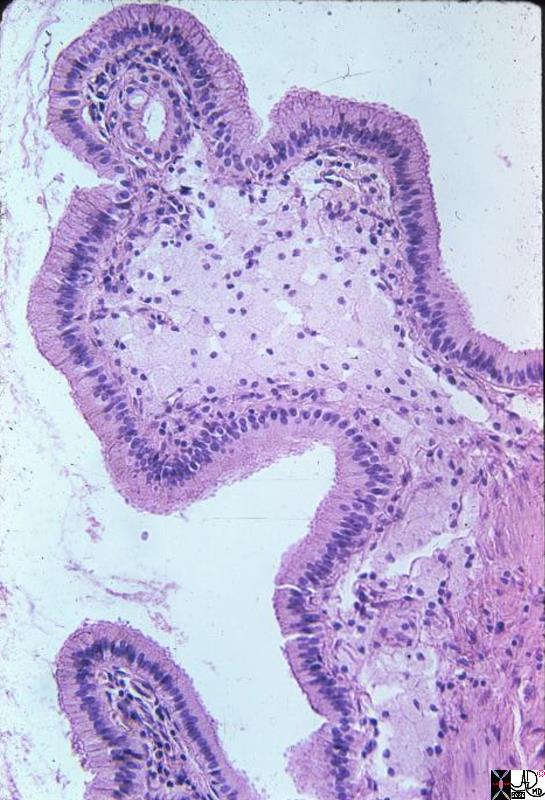 Phagocytosed Cholesterol Esters Phagocytosed Cholesterol Esters |
| This medium power photomicrograph shows a single mucosal frond distended by an aggregate of foamy macrophages. They are the pale cells in the center of the frond. Phagocytic histiocytes appear in H&E stained sections like large round (distended) cells with abundant cytoplasm. Phagocytosed particulate matter such as hemosiderin may be obvious and identifiable microscopically, but other substances such as mucin and lipids may simply make the phagocytes look “foamy” and delicate in the H&E section. In this gallbladder we can assume that the substance which has been phagocytosed by these histiocytes is lipid, probably cholesterol esters. The clue to this is the yellow color seen grossly.
gallbladder cholesterolosis histopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD 11936.8s |
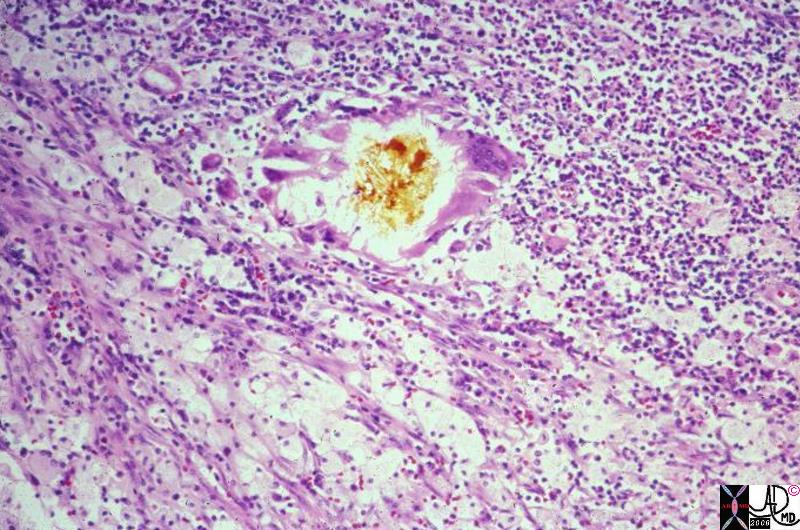
Bile Inciting Inflammation |
|
This photomicrograph shows a small piece of bile, in its yellow natural color, surrounded by foreign body type giant cells, surrounded in turn by a sea of WBCs and foamy histiocytes. The latter contain bile and lipid salts. The bile and the foamy histiocytes account for the yellow color seen grossly in xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. The “granulomas” are true foreign body-type granulomas composed of phagocytes trying to break down chunks of bile which have worked their way into the gallbladder wall during inflammatory disruption of the mucosa. 11938.8 gallbladder dx cholelithiasis histopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD |
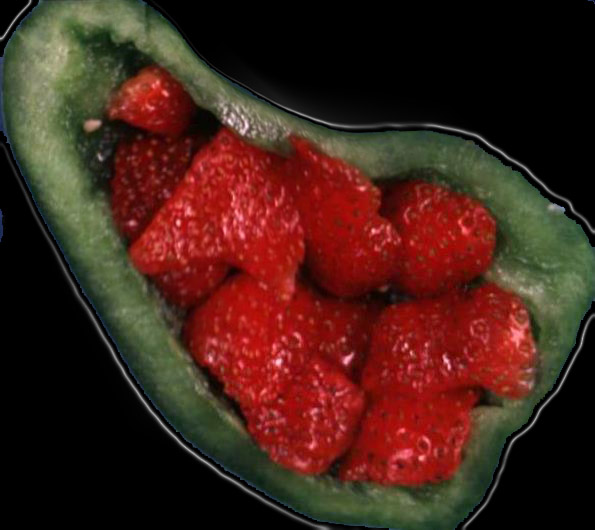
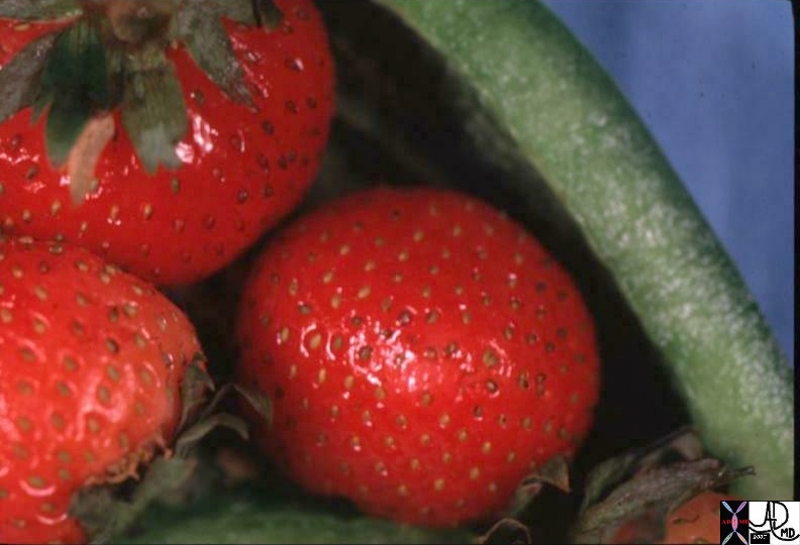
Strawberry Gallbladder |
|
The strawberries have been placed inside a green pepper. Note the similarity between the appearance of the outside of th estrawberry and the appearance of diffuse form of cholesterolosis. 04776b02 04761.800 gallbladder strawberry gallbladder greenpepper yellow cholesterolosis hyperplastic cholecystoses cholecytosis Davidoff Art hyperplastic cholecystosis hyperplastic cholecystoses adenomyomatosis cholesterolosis |
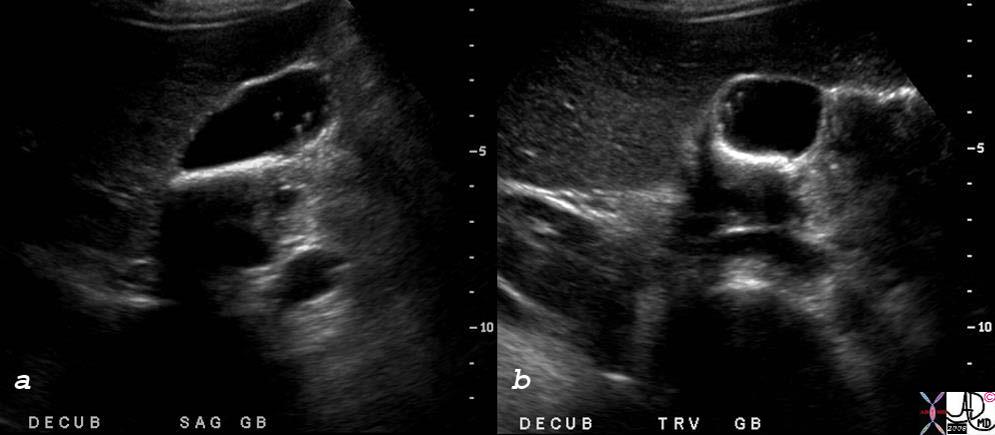
Echogenic Foci in the Wall with Ringdown Artifact |
|
Echogenic foci projecting into the lumen with ring down artifact are characteristic ultrasound findings of diffuse form of cholesterolosis.
82101cs 34 female gallbladder adenomyomatosis ring down artifact hyperplastic cholecystoses calcifications stones Aschoff-Rokitansky sinuses USscan ultrasound Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
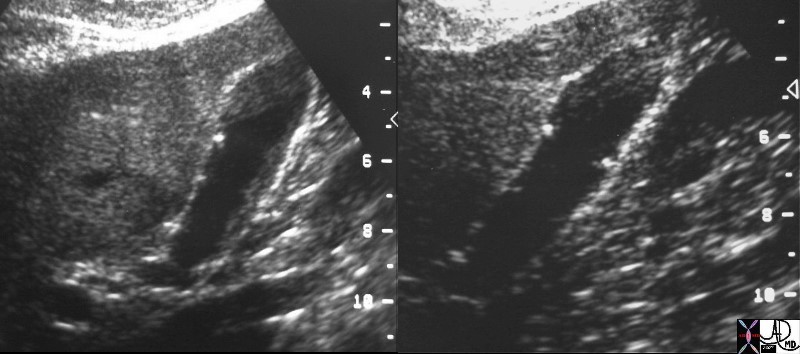
Echogenic Foci in the Wall with Ringdown Artifact |
| Non dependent echogenic foci projecting into the lumen with ring down artifact are characteristic ultrasound findings of the diffuse form of cholesterolosis A second example.
28345c01 gallbladder adherent polyps dx cholesterolosis hyperplastic cholecystoses dd papillomatosis US scan Davidoff MD |
 Hyperplastic Cholecystoses and Gallstones Hyperplastic Cholecystoses and Gallstones |
| Echogenic foci projecting into the lumen with ring down artifact are characteristic ultrasound findings of diffuse form of cholesterolosis. This US scan of non dependant echogenic foci of small echogenic polyps projecting into the lumen is characteristic of cholesterolosis. However dependant shadowing stones are seen in the neck as well.
78479c01.8s gallbladder outpouchings diverticula prominent Aschoff Rokitansky stones ring down artifact thickened wall hyperemic wall by doppler hyperplastic cholecystosis hyperplastic cholecystoses adenomyomatosis cholelithiasis shadowing USscan ultrasound courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
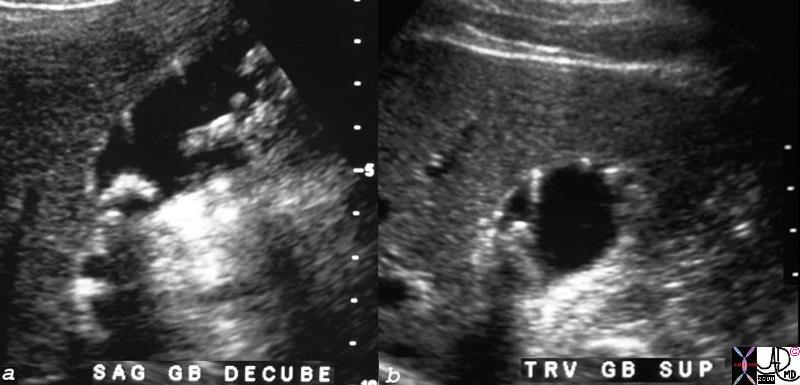
 Large Polyps Large Polyps |
| This form of cholesterolosis is characterized by elongated cholestsreol polyps which are a less common form of the disorder. These polyps may be elongated or round and can be up to 10mm long. When malignancy is a concern and in the differential diagnosis a PET scan helps to distinguish the two entities since cholesterol polyps are PET negative.
82195c01.8s 56M multiple polyps in the gallbladder gallbladder cholesterolosis or papillomatosis ring down artefact artifact hyperplastic cholecystoses USscan Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
|
|
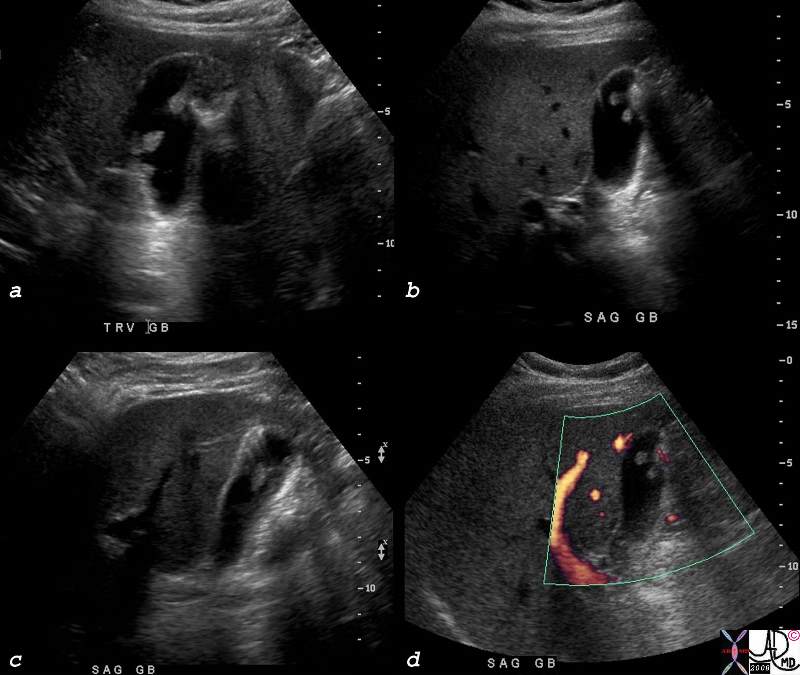
| Both cholelithiasis and cholesterolosis are common disorders but seemingly and surprisingly are not thought to have common etiological backgrounds. In this patient with calculous cholecystitis, non dependant choleterol polyps with ringdown artifact seen in a is associated with a hyperemic wall of acute cholecystitis in b.
78434c01s right upper quadrant pain positive Murphy’s sign gallbladder outpouchings diverticula prominent Aschoff Rokitansky stones ring down artifact thickened wall hyperemic wall by doppler hyperplastic cholecystosis hyperplastic cholecystoses adenomyomatosis acute cholecystitis USscan ultrasound courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
References
Poonam
Berk R N RN Berk, JH van der Vegt and JE Lichtenstein The hyperplastic cholecystoses: cholesterolosis and adenomyomatosis Radiology, Vol 146, 593-601,


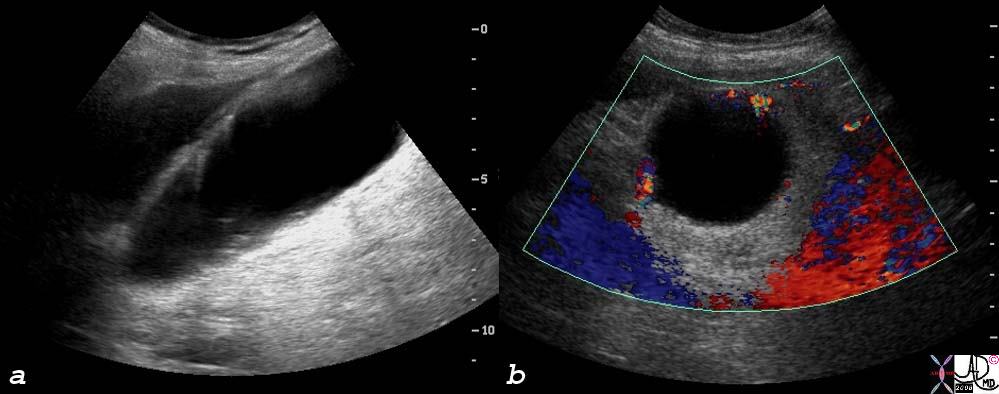 Hyperplastic Cholecystosis with Acute Cholecystitis
Hyperplastic Cholecystosis with Acute Cholecystitis