The Common Vein Copyright 2008
Alok Anand
Definition
Acute hemorrhagic cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease process of the gallbladder characterized by bleeding into the gallbladder or biliary system (hemobilia), often after trauma.
It is often caused by trauma to the biliary system, but may also be due to neoplasm, aneurysm rupture, ectopic gastric tissue. It is often associated with cholelithiasis as a source of traumatic injury. Although not a cause, anticoagulation therapy may pre-dispose patients to developing this disease.
This condition carries grave consequences, and often results with mortality. A less serious and rare consequence is ischemia of the gallbladder.
Structurally the gallbladder may be distended, with a thickened wall.
There is often no functional changes, although hemorrhage may result in a thrombus, which obstructs biliary flow, which may lead to cholestasis.
The clinical presentation of this disease process is very similar to acute cholecystitis. In addition to biliary pain there may be voimiting blood (hematemesis) and dark, bloody stools (melena), patients usually have a fever and elevated white cell count.
Hemorrhagic cholecystitis is diagnosed by radiographic imaging may show high attenuation on CT of gallbladder contents. There may be evidence of a complex cyst formation (intraluminal membranes), or a fluid-fluid level, owing to the different degrees of attenuation between blood and bile. MRI may show breakdown products of blood and can be used to estimate the age hemorrhage. HIDA Scan may show the absence of gallbladder
filling due to clot at or proximal to the cystic duct.
It is treated by surgical resection of the gallbladder, and repair of traumatic injury, if any. Because of the risk of mortality, conservative treatment with IV Fluids and antibiotics, as is often indicated in acute calculous cholecystitis, is appropriate.
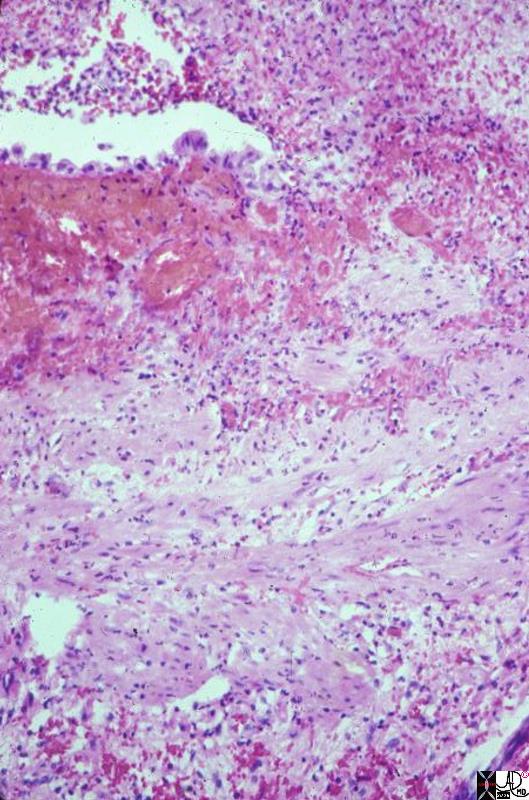
Acute Cholecystitis |
|
This is a high power photomicrograph of mucosa and muscular layer of a gallbladder with acute cholecystitis. Just a bit of the lumen is shown, indicated by the empty slit at one side of the picture. The fronds are flat, and a single layer of epithelium can be seen (at the edge of the slit). The epithelium is interrupted by acute inflammatory exudate which is extruding from the mucosa into the lumen. Hemorrhage is present beneath the epithelium, and there is acute inflammation through the wall. 11926.8s gallbladder cholecyctitis pathology histopathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD |
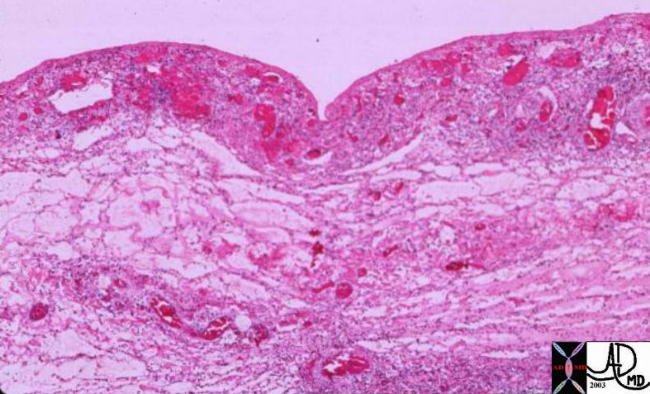
Hemorrhagic Congestion in the Gallbladder Wall |
| 00151 gallbladder wall inflammation acute cholecystitis histopathology |
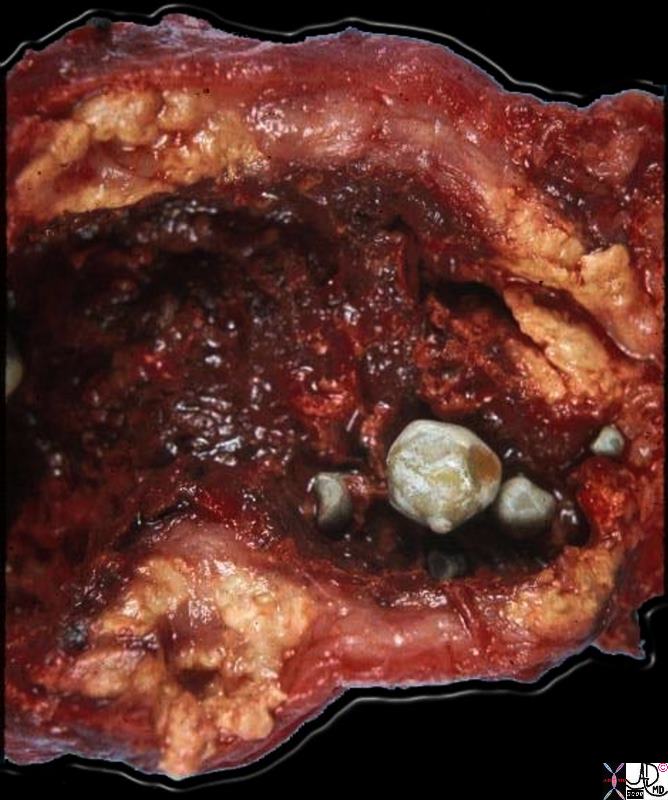
Hemorhagic Cholecystitis – Acute on Chronic |
|
This gallbladder was opended longitudinally to show the lumenal surface. Four gallstones are present. The mucosal surface looks hemorrhagic, indicative of active inflammation. The most striking aspect of this gallbladder is the marked thickening and yellow color of its walls. This is due to extrusion of bile into the wall during inflammation when the integrity of the mucosa is interrupted. Once in the tissues of the wall, the bile triggers an intense inflammatory reaction, and a response by histiocytes, which phagocytose the bile and attempt to break it down. The marked accumulation of lipids and their break-down products imparts the yellow color. The significance of this variant of chronic cholecystitis is that it mimicks carcinoma by the way it thickens the wall. The radiologist, the surgeon, and even the pathologist may think this is carcinoma until the microscopic sections are examined. 11937b01.8s gallbladder dx cholelithiasis grosspathology Courtesy Barbara Banner MD |
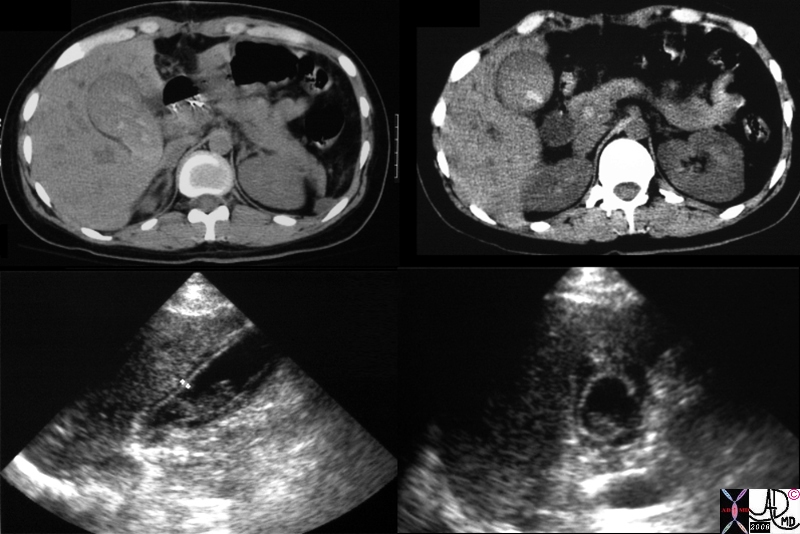 Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis |
| 16214c.8s gallbladder distended enlarged containing hyperdense material sludge differential diagnosis tumefactive bile cholestasis dx acute hemorrhagic cholecystitis CT scan USscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 200 |
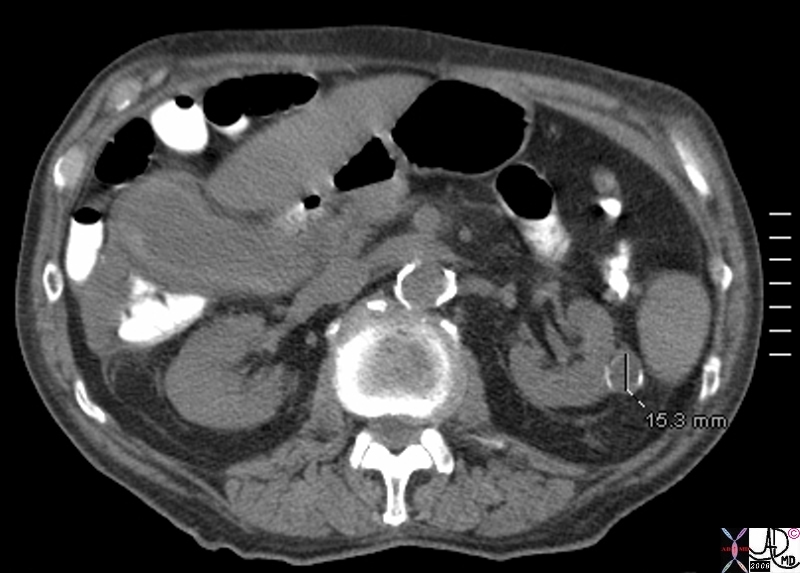 Acute Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis Acute Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis |
| 81902s.8b01 elderly man with acuteright upper quadrant pain gallbladder wall mildly distended gallbladder hyperdense irregular wall dx acute hemorrhagic cholecytitis acute on chronic cholecystitis kidney cyst complex calcification grade 3 Bosniak CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
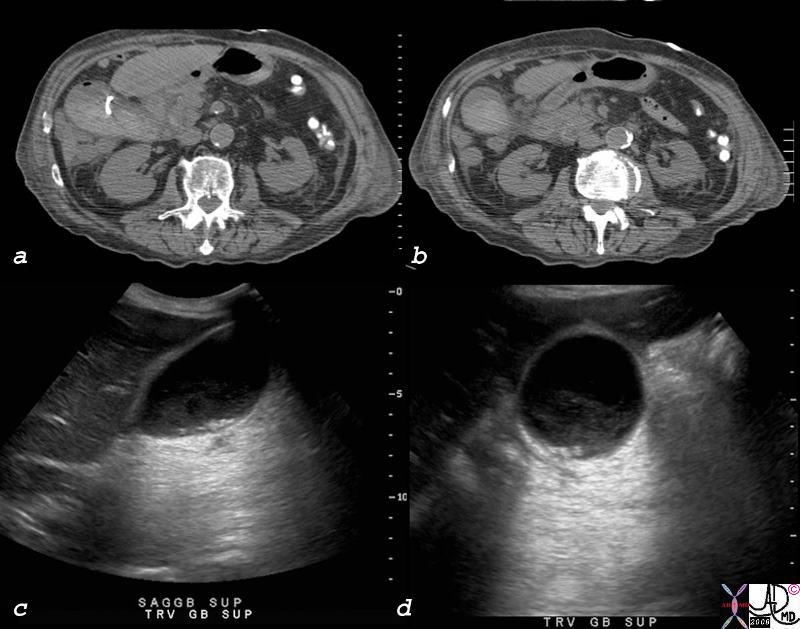 Acute Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis Acute Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis |
| 81902c02.8s elderly man with acuteright upper quadrant pain gallbladder wall mildly distended gallbladder hyperdense irregular wall dx acute hemorrhagic cholecytitis acute on chronic cholecystitis kidney cyst complex calcification grade 3 Bosniak CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
References
eMedicine: Acute Cholecystitis
BrighamRad Hemorrhagic Cholecystitis
Reference: Chinn et al. “Hemorrhagic cholecystitis. Sonographic appearance and clinical presentation.” 1987
