Neck
The neck is the smallest part of the gallbladder both in diameter and in volume. It tends to be sigmoid in shape and at its most medial end it turns inferiorly as it joins the cystic duct. Sometimes a fold is found on the posterior wall of the gallbladder where the body and neck join. This fold is called a junctional fold and has no clinical significance.
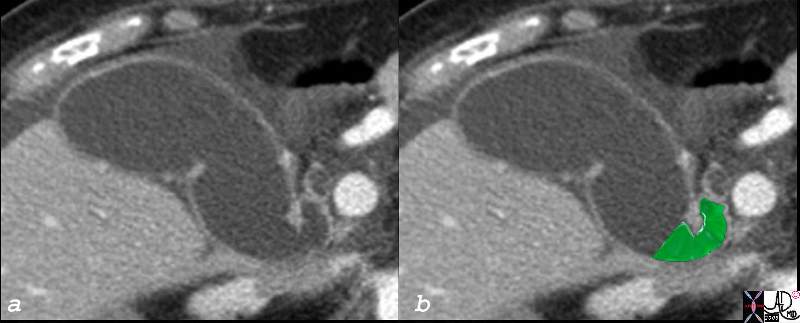
Neck of the Gallbladder |
| The neck of the gallbladder is sually quite difficult to image. In this CTscan of an elderly fenmale patient the gallbladder is dilated so its component parts are distorted and easierto visualise. The partial sigmoid shape of the neck is overlaid in green.82382c03.8s 82382c03 85F gallbladder shape neck of the gallbladder cystic duct size age time distended dilated parts fundus body neck infundibulum cystic duct distended dilated small amount of fluid in the gallbladder fossa ascites CTscan copyright 2008 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
It is the most medial part of the gallbladder and lies in close association with the porta hepatis.
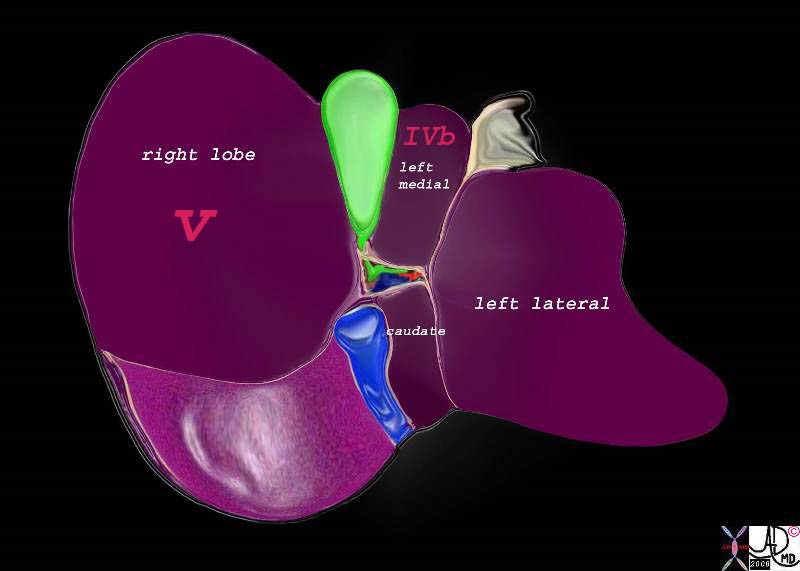
Relationship of the Neck to the Porta Hepatis |
|
The neck is the most posterior and medial portion of the gallbladder and is in close association with the porta hepatis which lies even more posterior and medial to it. 82220b01.2k05.82s liver gallbladder porta hepatis hepatic artery portal vein IVC inferior vena cava falciform ligament ligamentum teres bare area of the liver left lobe segment IV segment I caudate lobe quadrate lobe medial segment left ;obe lateral segment left lobe gastrohepatic ligament gallbladder right lobe hepatic Davidoff art copyright 2008 |
Applied Biology
The full extent of the neck is not routinely visualized on US because of its smal size, tortuosity and the fact that is nestled deep among other structures .
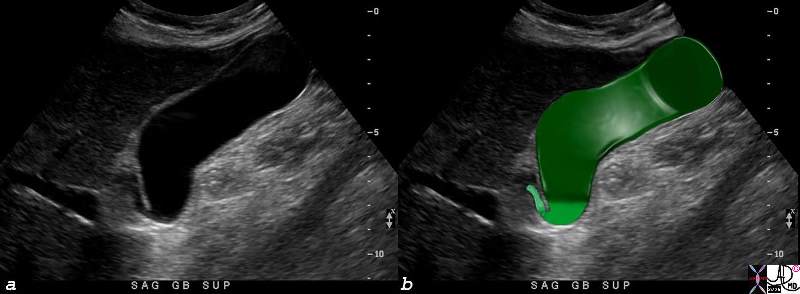
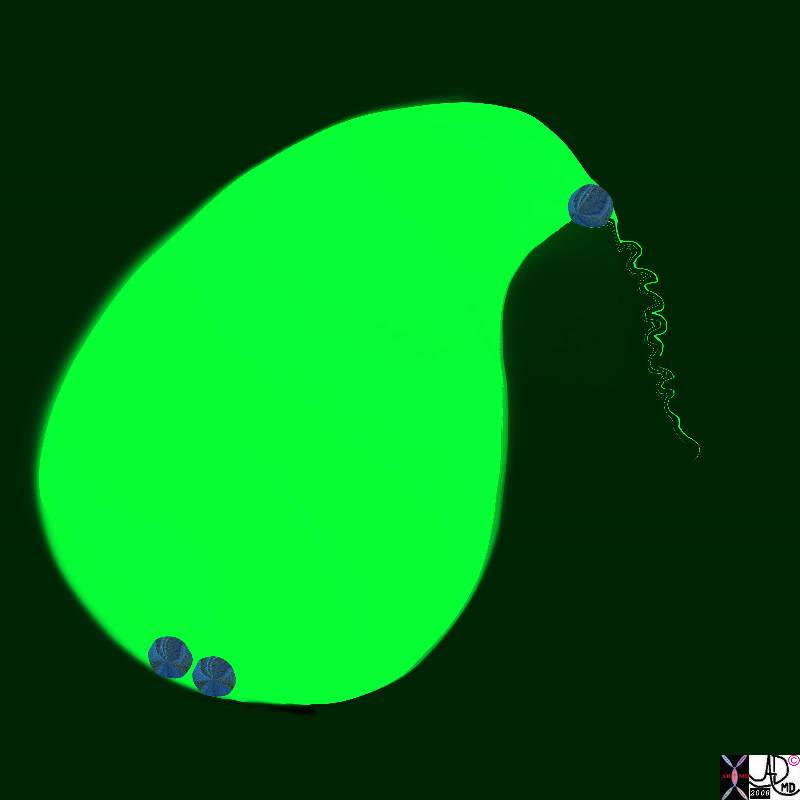
Parts of the Gallbladder – Ultrasound |
| The full extent of the neck of the gallbladder is not easily nor routinely seen on all ultrasound examinations because it is small, tortuous, and nestled among other echogenic structures that tend to camouflage it. In this instance, the neck (lightest green can be seen between the infundibulum and the beginning of the cystic duct.82416c04.8s gallbladder parts fundus = darkest green body = dark green neck = light green cystic duct = lightest green normal anatomy USscan ultrasound Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
As the structure with the smallest diameter and most tortuous course, it is the site that has a predilection to stone impaction.

Stone Impacted in the Neck Causing Obstruction |
|
The neck of the gallbladder is the narrowest and most tortuous portion of the gallbladder and thus there is a predilection for stones to become impacted and cause obstruction. If the obstruction is complicated by inflammation then acute cholecystitis ensues. 11921.8b05b019.8s gallbladder cystic duct gallstones cholelithiasis stone impacted in the cystic duct distended enlarged Davidoff Art copyright 2008 |
Hartmann’s pouch (aka ampulla of the gallbladder, fossa provesicalis, pelvis of the gallbladder) is a spheroidal or conical pouch at the junction of the neck with the cystic duct. It is a outpouching on the inferior surface of the neck that is thought to be acquired during life and caused by stone disease resulting in inflammation and secondary adhesions between the neck and the cystic duct.
References
Cystic Duct
Turner MA Fulcher AS The Cystic Duct: Normal Anatomy and Disease Processes Radiographics. 2001;21:3-22
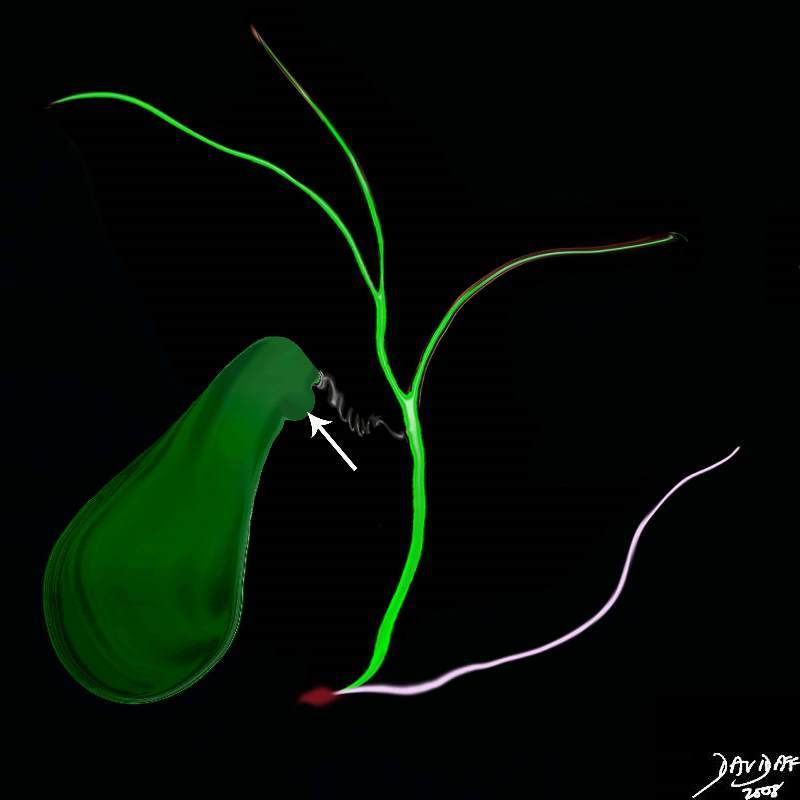
Hartmann’s Pouch |
| Hartmann’s pouch (arrow) is an outpouhcing situated on the inferior aspect of the neck of the gallbladder that is caused by prior inflammatory and stone disease in the area.04766b05b07.32k.8s Hartmann’s pouch infundibulum anatomy stone disease acquired gallbladder Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
