Choledocholithiasis |
|
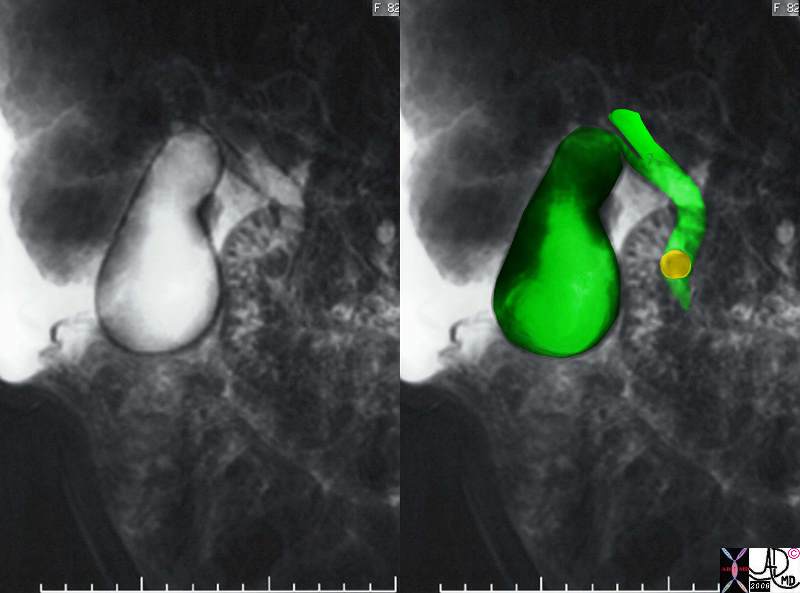
The MRCP performed using T2 weighted FSE technique shows a CBD stone (orange) associated with dilatation of the CBD, cystic duct and the gallbladder. 17083c02.3k.8s 82 female presents with obstructive jaundice gallbladder duct enlarged distended distension dilated dilatation choledocholithiasis stone obstruction obstructive jaundice MRI T2 weighted Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
Trauma
Traumatic injury is a form of mechanical injury where the inciting aggressive force is from the external environment. The cause is either via blunt or penetrating mechanism and it results in tearing, shearing, or fracture of the tissues.
Structurally the injuries range from mild swelling or bruising to extensive tearing and even rupture of the organs.
Functionally impairment varies from minimal to mortal consequences.
The diagnosis is based mostly on the history, and the extent of injury is evaluated from a clinical and imaging standpoint.
Treatment depends on the extent and location of injury but surgery is the most common form, with medical treatment used for supportive measures.
Trauma to the gallbladder is relatively uncommon because of the position of the gallbladder and its protection by the liver.
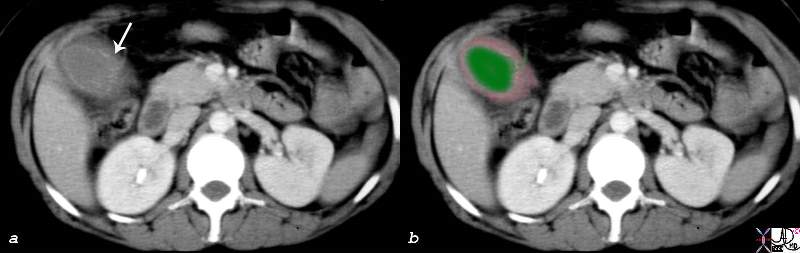
Gallbladder Laceration from Trauma |
| The 32 year old male suffered from a motor vehicle accident and presented with right upper quadrant pain. The gallbladder shows disruption of the mucosal enhancement (arrow in a) and is thick walled (pink) These findings are consistent with a a laceratio and possible rupture of the gallbladder.
16216c01.8s 32 male s/p trauma MVA gallbladder hyperemic mucosa thickened wall disrupted mucosa decompresssed lumen CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
Metabolic Disease
Metabolic disease is the aberration of the biochemical mileu of the body caused by aberrant absorbtion, aberrant control mechanisms such as endocrinolgical disease, or aberrant excretion of chemicals or water from the organs or the body.
Structurally the biochemical changes more commonly than not do not have structural change at a macroscopic level, but endocrinological diseases such as Grave’s disease, gigantism, and Cushing’s disease do have characteristic and distinct structural manifestations.
Functionally the effects are far reaching and variable depending on which of the many complex chemicals is involved.
The diagnosis is made usually by evaluation of the body fluids.
Treatment is based on the cause of disease.
The gallbladder sometimes is the harbinger of gallstones caused by abnormal cholesterol metabolism or by excessive aberrant metabolism that causes pigmented stones.
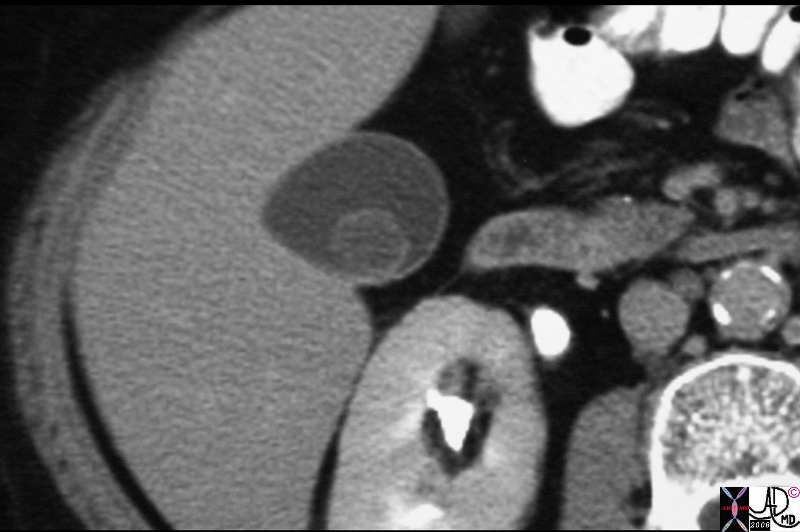
Low Density Cholesterol stone |
| The CTscan through the gallbladder shows a relatively large (approximately 1cms) low density stone with minimal rim calcificationlying dependantly in the body of the gallbladder. This finding is reminiscent of a cholesterol stone.
25566.8s gallbladder stone low density filling defect cholelithiasis cholesterol Cpourtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2008 |
Circulatory Disease
Circulatory disease is an aberrance of any part of the structures of the circulation but usually inferring disease of the arteries or veins. Causes for diseasese include thrombosis, embolisation, aneurysmal disease, arteriovenous malformation, congestion, ischemia, or infarction.
The structural changes are manifest in the vessel involved and sometimes at the end organ level as well.
The functional changes vary between minimal effects such as in varicocties, to life threatening situations such as in coronary thrombosis, or ruptured aneurysm.
Diagnosis is a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging manifestations. Angiography used to be the mainstay of diagnosis of circulatory disease, but CTscans and MRI are evolving as major tools since they are able to evaluate both the vessels and the end organ to better effect.
Treatment is based on the disease, but newer techniques in the minimally invasive sphere have become imporant including thrombolyis, vessel stenting and angioplasty.
The gallbladder has an endarterial blood supply so that the fundus is the most vulnerable part. When the gallbladder becomes distended, pressure on the vessel wall can result in ischemic necrosis with rupture of the wall usually at the fundus.
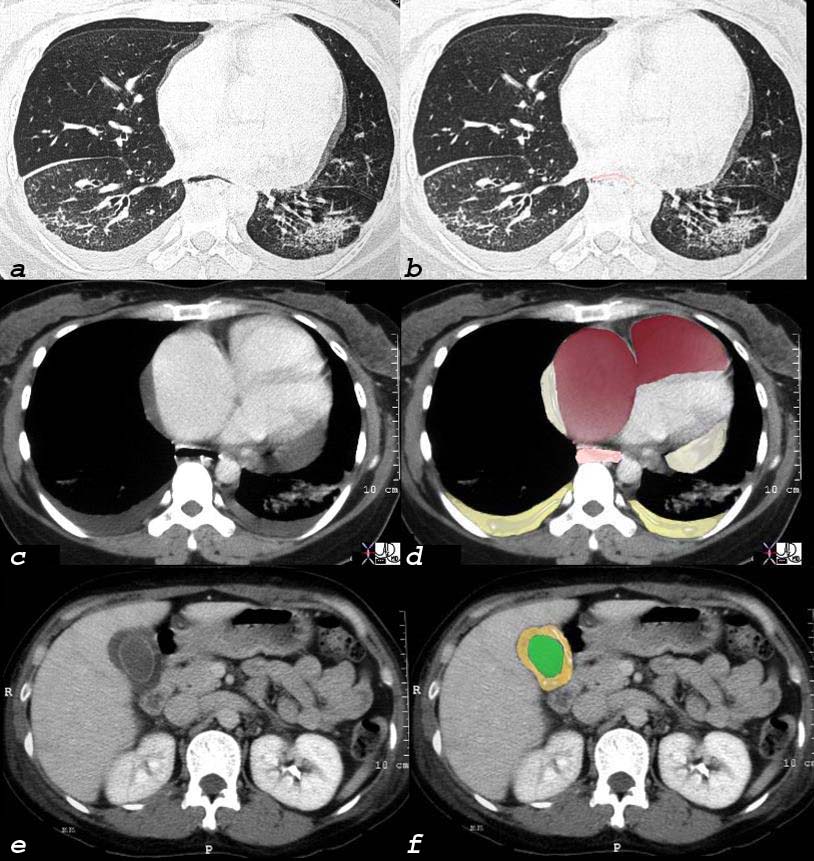
Scleroderma Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Heart Failure |
|
This 32 year old female has scleroderma and her disease is characterized by interstitial basal lung disease (a,b) with normal anterior lung fields and fibrotic posterior lung fields, enlargement of right heart structures (maroon in d), pericardial effusion (light yellow in d), pleural effusions (dark yellow in d) and an edematous wall (orange, in f) of the gallbladder (lumen is green). As a result of her lung disease she developed pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure and tricuspid regurgitation and this lead to the gallbladder edema. This is a issue of congestion of the hepatic venous syustem causing congestion of the gallbladder drainage and subsequent result of gallbladder wall edema. and 30464c08 32 female lungs pleura heart cardiac RA RV right ventricle right atrium pericardium gallbladder esophagus ILD basal interstitial lung disease pericardial effusion pleural effusion cardiomegaly enlarged esophagus patulous esophagus gallbladder wall edema congestive cardiac failure RHF right heart failure pulmonary hypertension cor pulmonale dx scleroderma CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
Iatrogenic disease
Iatrogenic disease is disorder induced by physicians and includes causes such as negative effects of drugs, errors in surgery, hospital acquired infections, and medication errors.
The resulting disorders are varied and the structural, functional results and diagnostic and therapeutic challenges are equally varied.
Laparoscopic surgery on the gallbladdder by inexperienced surgeons may result in bile duct injury which complicates recovery and requires further surgery to repair the ducts.
Immune disease
Immune disease incorporates aberrant allergic immune response to noxious agents in the environment including microorganisms, pollen or dust, as well as the autoimmune diseases where the aberrant immune system fails to recognize host tissue.
The cause for these responses is in general not known, and the structural result ranges from muscle spasm, to anaphylaxis, to acute and chronic inflammation.
Functionally the range of disorders includes bronchospasm, edema, hypotension in the anaphylaxis/allergic group, to chronic debilitaion and multisystem dysfunction in the autoimmune group.
Treatment is medical and is in general antiinflammatory in nature.
The gallbladder is not usually involved in immune disease.
Idiopathic Disease
Idiopathic disease is a disease of unknown cause
Functional Disorders
Functional disorders are diseases that arise from aberrant function that does not have an obvious structural basis.
The hyperplastic cholecystoses are a range of diseases that appear to have a functional basis possibly related to hypercontractile disorders of the gallbladder.
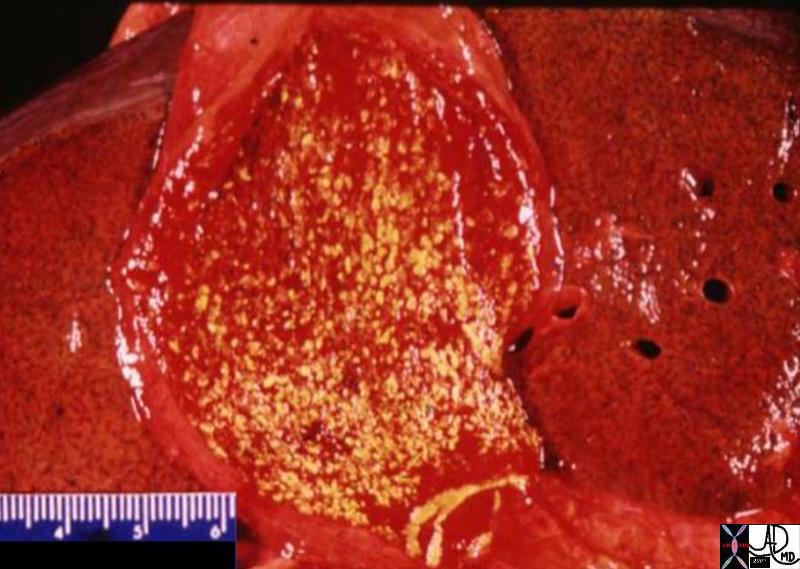
Strawberry Gallbladder |
|
The dramatic pathology image shows an opened gallbladder stippled with yellow fatty deposits of cholesterol, in a background of a hyperemic red mucosa, that is characteristic of the strawberry gallbladder. Strawberry gallbladder is on of the entities that belong in the group of diseases of the gallbladder called the hyperplastic cholecystoses which appear to be related to a hypercontractile state. hyperemic 04777.800 gallbladder strawberry gallbladder hyperemic mucosa yellow cholesterolosis hyperplastic cholecystoses cholecytosis Davidoff MD hyperplastic cholecystosis hyperplastic cholecystoses adenomyomatosis cholesterolosis |
