Fundus
The fundus has the largest diameter, is usually spherical in shape, is the only portion of the gallbladder that is exposed and unprotected by the liver. It lies as the most anterior and rightward portion of the gallbladder. It lies superior to the hepatic flexure. As the most inferior portion of the gallbladder it is the most dependant part during the day while the person is upright. Hence the bile that is most concentrated with the highest SG will be found in the fundus. The blood supply is endarterial meaning it is the last part of the gallbladder to receive its blood and therefore it is most vulnerable to ischemia. It is the only portion of the gallbladder that is completely surrounded by peritoneum. Since it is not attached to the liver it is relatively mobile so that when the gallbladder stretches in atonic conditions such as old age, it is mostly the fundus that stretches.
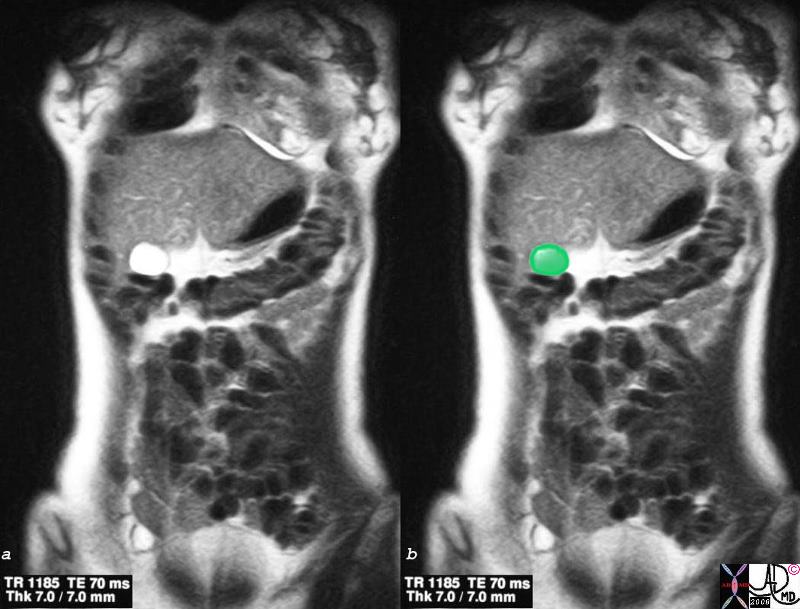 The Fundus as the Only Exposed Portion of the GallbladderAnterior Coronal View of the Gallbladder – MRI The Fundus as the Only Exposed Portion of the GallbladderAnterior Coronal View of the Gallbladder – MRI |
| Just beyond the liver edge in the midclavicular line, and just below the 9th right rib, the fundus of the gallbladder lies unprotected and potentially palpable to the examining hand. However it is not normally palpable unless it is significantly distended. The body and neck lie more posterior and inaccessible to clinical examination even when enlarged.26629c.8s gallbladder liver normal anatomy fundus exposed anterior cut MRI T2 weighted Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
Applied Biology
The fundus is the only part of the gallbladder that potentially is clinically palpable, and in fact is only palpable when the gallbladder is significantly distended. When the pressure in the gallbladder rises the tension on the fundus will be maximal according to the law of Laplace since the tension on the wall for a given pressure is directly proportional to radius. Therefore the fundus with the largest radius will enlarge out of proportion in relation to the body and the neck. The site of rupture from distension therefore will also be the fundus not only because it has the most tension exerted on it but also because it is supplied by an end artery.
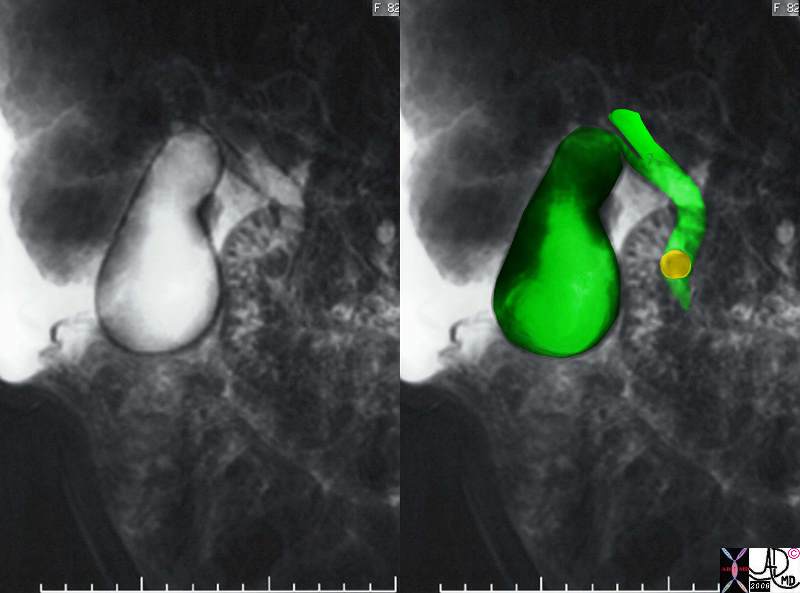 Fundal Enlargement Fundal Enlargement |
| The MRCP performed using T2 weighted FSE technique shows a CBD stone associated with dilatation of the CBD, cystic duct and the gallbladder. The shape change of the enlarged gallbladder is most profound in the fundus because of the increasesd tension exerted on the largest diameter of cylinder/sphere according too Laplace’s law.17083c02.3k.8s 82 female presents with obstructive jaundice gallbladder duct enlarged distended distension dilated dilatation choledocholithiasis stone obstruction obstructive jaundice MRI T2 weighted Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 |
